Blogs
Qubit by Qubit in Quantum Supremacy
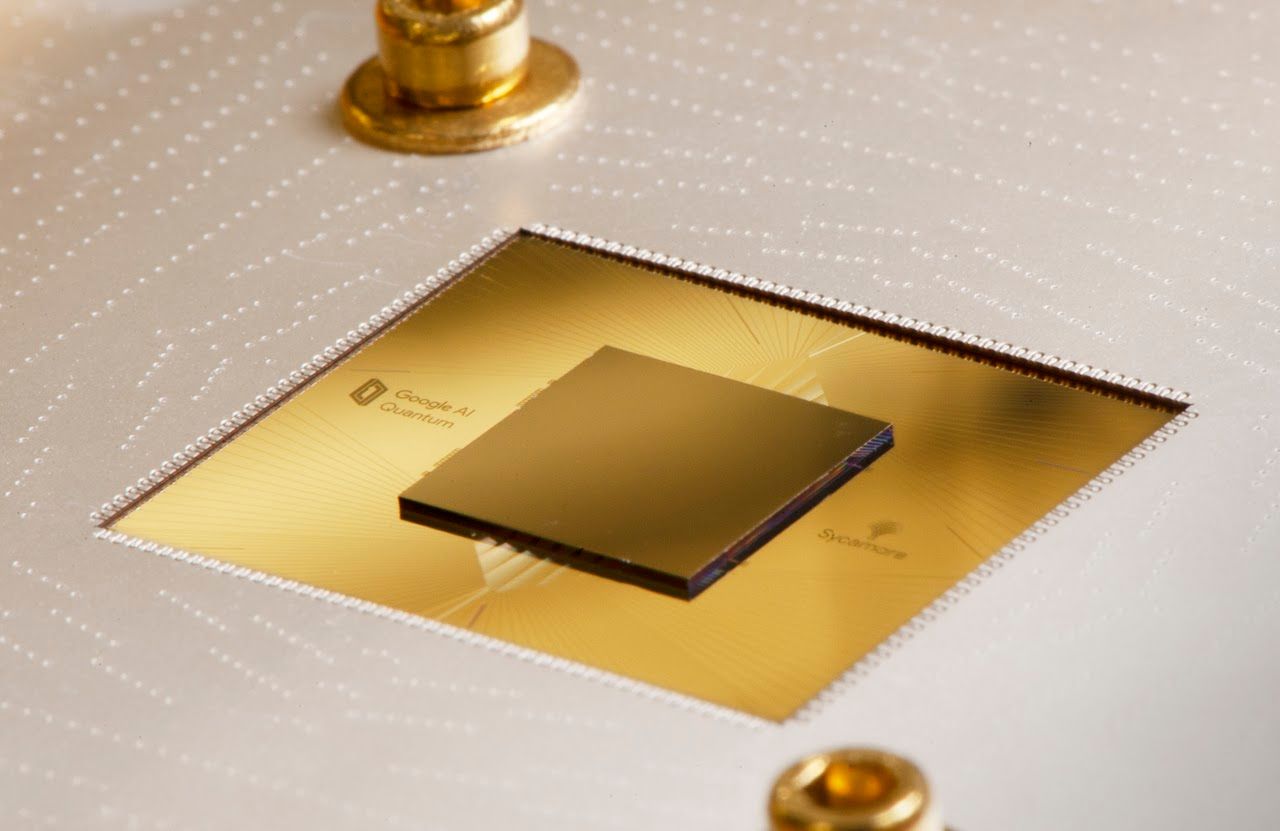

In October 2019, Google made a groundbreaking announcement: they had achieved quantum supremacy. This milestone marks a pivotal moment in the history of computing, signalling a future where quantum computers could outperform the most powerful classical supercomputers on specific tasks. But what exactly is quantum supremacy, and why does it matter?
Understanding Quantum Supremacy
Quantum supremacy occurs when a quantum computer can perform a calculation that is infeasible for any classical computer to achieve in a reasonable time. Google's quantum processor, Sycamore, reportedly performed a task in 200 seconds that would take the world's fastest supercomputer, Summit, approximately 10,000 years to complete. This is a monumental leap forward, but it's essential to note that the task solved was highly specialised and not of practical use. However, it demonstrates the potential power of quantum computing.

Why Quantum Supremacy Matters
- Unprecedented Computational Power: Quantum computers leverage the principles of quantum mechanics, such as superposition and entanglement, to process information in fundamentally new ways. This enables them to solve complex problems exponentially faster than classical computers.
- Reimagining Industries: In chemistry, it can simulate molecular structures and interactions at an unprecedented level, leading to breakthroughs in drug discovery and materials science. In logistics and finance, it can optimise complex systems and solve intricate problems that are currently intractable.
- Advancing Artificial Intelligence: Quantum computers can enhance machine learning algorithms by processing vast datasets more efficiently and finding patterns that classical computers might miss. This could accelerate advancements in AI and lead to more sophisticated and capable AI systems.
- Cryptography: Quantum computers could potentially break widely-used encryption methods, prompting the need for quantum-resistant cryptographic algorithms to ensure data security in the future.
Challenges and the Road Ahead
While the achievement of quantum supremacy is a significant milestone, the road to practical and widespread quantum computing is still long. Several challenges need to be addressed:
- Error Rates: Quantum systems are highly susceptible to errors due to decoherence and noise. Developing error-correcting codes and more stable qubits is crucial for building reliable quantum computers.
- Scalability: Current quantum processors have a limited number of qubits. Scaling up the number of qubits while maintaining their coherence and connectivity is a significant engineering challenge.
- Practical Applications: Identifying and developing practical applications for quantum computing that can solve real-world problems is essential for its widespread adoption.
Despite these challenges, the race towards quantum computing continues to accelerate, with significant investments from governments, corporations, and research institutions worldwide. Quantum supremacy is just the beginning—it's a glimpse into a future where quantum computers could unlock new possibilities and transform the technological landscape.